The most common form in which it is found is as an alloy, which also typically consists of other elements such as iron, manganese, magnesium, silicon, zinc, and copper in varying proportions. The most common form in which it is found is as an alloy. Using this substance in the form of various alloys is by far its most common application. It is possible that the inclusion of these components will lead to an increase in the overall tensile strength of the product once it has been manufactured. In addition, it is possible that these components will contribute other beneficial properties, such as improved electrical or thermal conductivity. This is something that we will discuss in more detail later. The production of a wide variety of components, such as those used in the automotive, power transmission, electronics, computing, and telecommunications industries, amongst others, requires the use of aluminum alloys.
For the purpose of accurately describing the make-up of wrought iron metal alloys and castings, a specialized numerical identification system is utilized. This method is applied to the production of aluminum alloys in addition to wrought iron alloys. One is able to provide a classification for the wide variety of aluminum alloys that can be produced by making use of this system.

The initial digit serves not only as an indication of the primary alloy(s), but also as a representation for the overall class or series. Before the numerical description of the particular alloy, the modifications that were made to it are denoted by a lowercase letter followed by an uppercase letter that is placed before the numerical description. An aluminum casting will always have a.0 at the very end of the piece.
Pure aluminum alloys, heat treatable alloys, and non-heat treatable alloys are the three categories that are typically used in commercial specifications to classify the many different types of aluminum alloys that are available to consumers. Non-heat treatable alloys are alloys that cannot be subjected to heat treatment in any way. Alloys that are not capable of being heat treated are referred to as "non-heat treatable."
Pure Aluminum Alloys
Alloys made of pure aluminum, such as those in the 1xxx series, contain at least 99.9 percent pure aluminum, which is aluminum in its purest, most unaltered form. In addition to providing superior protection against corrosion, these items also exhibit superior workability and weigh only a moderate amount. One of their most common uses is in transmission lines and another is in power grid lines.
Materials That Are Able to Go Through the Process of Heat Treatment Alloys
After an initial heating process, particular kinds of aluminum alloys can have their strength increased by undergoing heat treatments such as quenching or rapid cooling, both of which come after the heating process itself. In general, these metals are categorized as belonging to either the 2xxx series (which contains significant quantities of copper), the 6xxx series (which contains compounds of magnesium silicide), or the 7xxx series (which contains significant quantities of zinc). Each of these series contains significant quantities of one of those elements. However, there are a few alloys in the 4xxx series that can be heat treated, whereas the vast majority of alloys cannot be heat treated. The vast majority of alloys, however, cannot be heat treated. The vast majority of alloys are not capable of undergoing heat treatment.
Alloys That Do Not Require the Processing Steps to Be Carried Out at a High Temperature
When working with alloys that cannot be heat treated, one is typically required to use techniques of cold working, such as rolling or forging. Alloys in the 1xx series, which contain pure aluminum; alloys in the 3xx series, which contain manganese; alloys in the 4xx series, which contain silicon; and alloys in the 5xx series, which contain magnesium are examples of the types of alloys that fit into this category. However, this list is not exhaustive.
Aluminum Casting
Casting in aluminum continues to be the method that is both the most well-established and the most well-known method for producing high-quality precision parts at a low cost. The reason for this is due to the fact that casting in aluminum has been around for a very long time. During this stage of the process, the desired form is recreated by pouring molten metal into a mold in order to cast it. After that, the form is released from the mold it was created in. The composition of the alloys that are used in the manufacturing process of these metal parts is what determines the desirable properties that are exhibited by the finished products, and this composition is determined by the alloys themselves. Take, for example:Some of the characteristics that may be present include low weight, resistance to high temperatures and corrosion, ability to conduct electricity, high strength, and favorable finishing characteristics. Additional possible characteristics include a high level of strength as well as favorable finishing qualities.
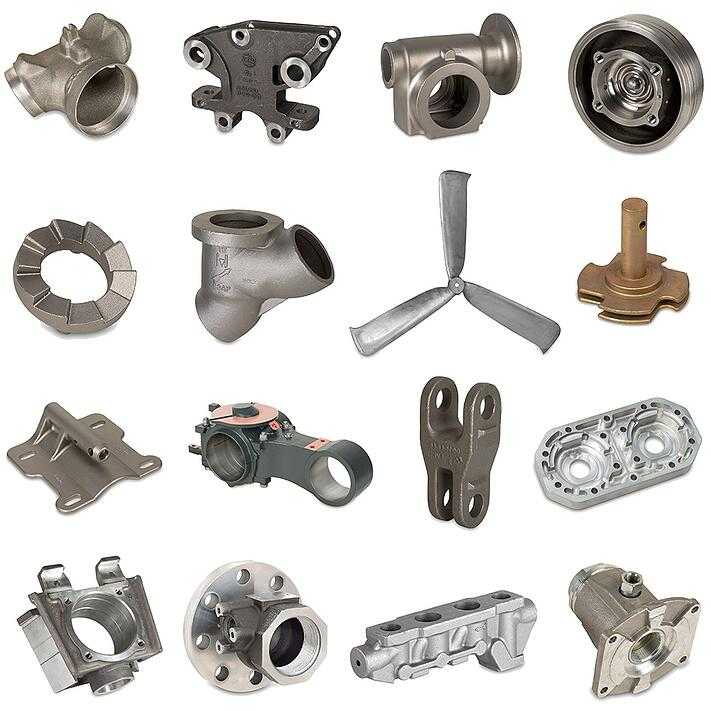

In order to provide the utmost level of convenience for Bunty LLC's clientele, the aluminum casting services that are provided by Bunty LLC can be separated into four distinct categories. The selection of aluminum alloys is typically determined by a number of factors, the most important of which are the desired casting process of the customer, the relative difficulty of the casting design, the availability and cost of a particular alloy, and any other relevant considerations. In our facilities, casting processes such as the ones listed below are carried out:
Putting Theories to the Test in the Sand
In spite of the process's adaptability, affordability, and relative sluggishness, the intricate surface designs can be faithfully reproduced using this casting method. Other advantages of the method include:It is possible to cast parts of any size, including those that are extremely large, as a result of this capability. This designation is applicable to a wide variety of alloys, including A356.0, C355.0, 357.0, 443.0, 520.0, and 713.0, to name a few.
Casting That Is Done Through Investment Is Called Investment Casting.
The process of investment casting makes it possible to create intricate shapes out of virtually any alloy. Additionally, investment casting is capable of producing superior exterior surfaces, which frequently eliminates the need for additional finishing steps. The following are examples of alloys that are currently available:208.0, 295.0, 308.0, 355.0, 356.0, 443.0, 514.0, 535.0, 712.0
The process of die casting can be carried out either under high pressure or under low pressure.
We are applying pressure to the steel die that is being used in this process of casting in order to force the molten metal into the die so that we can inject molten metal into the die. This process is called "casting."It is suited for high-volume production methods that require only a minimal amount of machining and finishing of the parts, and these production methods are suited for the use of this material because it is suited for high-volume production methods. The following are examples of alloys that are currently available:A380.0, 360.0, 380.0, 413.0, 518.0
Casting is done using a technique called gravity die casting, which is also called permanent mold casting.
We use this casting method in conjunction with steel (or other metals) cores and molds in order to produce components that are more long-lasting than those that we could make utilizing the sand casting or die casting processes. Specifically, we are able to do this because this casting method allows us to produce components that are cast in a way that allows us to cast in a way that allows usThe following alloys can be produced using this material: A356.0, A357.0, B443.0, C355.0,355.0,356.0, 366.0, and 513.0.